co2 electron pair geometry and molecular geometry|CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar : Clark The molecular Geometry of any compound is based on the arrangement of atoms, electron pairs, and bonds. Here in CO2, both Oxygen atoms form sigma bonds with the central carbon atom and complete their octet. As a result, there are no lone pairs of . Tingnan ang higit pa Watch and Download free Kerala Tulasi All 60 Videos Compilation Part 1 porn video
PH0 · Predicting Electron
PH1 · Electron Geometry for CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
PH2 · Electron Geometry VS Molecular Geometry
PH3 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar
PH4 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
PH5 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Geometry, and
PH6 · CO2 Lewis Structure,
PH7 · 8.6: Molecular Geometries
PH8 · 7.2 Electron Pair Geometry versus Molecular Structure
PH9 · 5.9: Molecular Geometry
“DocTract is an easy to use policy management system. The product does a great job of integrating the policy revision/creation process with the public facing portal...The product is also a good value.”
co2 electron pair geometry and molecular geometry*******CO2 Molecular Geometry. The molecular Geometry of any compound is based on the arrangement of atoms, electron pairs, and bonds. Here in CO2, both Oxygen atoms form sigma bonds with the central carbon atom and complete their octet. As a result, there are no lone pairs of electrons, but . Tingnan ang higit paOne needs to know the Lewis structure in order to understand the molecular geometry of any given molecule. This structure . Tingnan ang higit pa
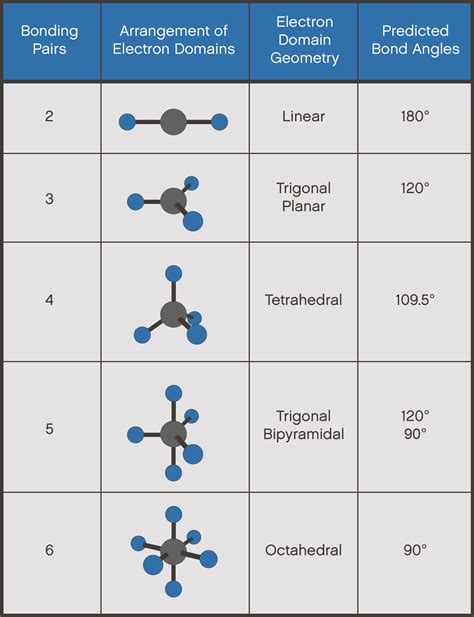
The electronic configuration of the Carbon atom in its ground state is 1s22s22p2, and that of an Oxygen atom is 1s22s2p4. When the electrons are in an excited state, they jump to other orbitals. In its excited state, the atom’s electronic configuration becomes . Tingnan ang higit paThe molecular Geometry of any compound is based on the arrangement of atoms, electron pairs, and bonds. Here in CO2, both Oxygen atoms form sigma bonds with the central carbon atom and complete their octet. As a result, there are no lone pairs of . Tingnan ang higit paCO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar Contents show. CO2 Lewis Structure. The lewis structure of CO2 can be with some simple steps, but before that, it is important to understand lewis structure properly. . Because the Carbon dioxide molecule has two electron domains (two oxygen atoms and n. Valence shell electron-pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory) enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule or a .
In calculating electronic geometry we use the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model, which states that the lowest geometry for electronic orbitals around a positive nucleus is for the orbitals to be .Lewis Structure of Carbon Dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a colourless, odourless, incombustible gas produced by the combustion of carbon. The carbon-oxygen ratio in a CO 2 molecule is 1:2. Two double bonds . CO2 Molecular Geometry & Shape. In a CO2 molecule, the carbon atom is in the center double bonded with two oxygen atoms by each side. Both oxygen atoms have two lone pairs of nonbonding .
The C in CO 2 has a linear electron-pair geometry and a linear molecular structure/shape. Both of these are the same since there are no lone pairs on the C .
Learning Outcomes. Explain the concepts of polar covalent bonds and molecular polarity. Electron-Pair Geometry versus Molecular Structure. It is important to note that .
Electron Geometry VS Molecular Geometry - The key difference between electron geometry and molecular geometry is that electron geometry is found by utilizing both single electron combines and .co2 electron pair geometry and molecular geometry CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar Since water has two lone pairs it's molecular shape is bent. According to the VSEPR theory, the electrons want to minimize repulsion, so as a result, the lone pairs are adjacent from each other. CO 2: Carbon dioxide has two electron groups and no lone pairs. Carbon dioxide is therefore linear in electron-group geometry and in molecular .Figure 7.2.2. (a) The electron-pair geometry for the ammonia molecule is tetrahedral with one lone pair and three single bonds. (b) The trigonal pyramidal molecular structure is determined from the electron-pair . CO2 has a total of 16 valence electrons (carbon has 4 and oxygen 6 valence electrons). CO2 has a linear molecular geometry with a bond angle of 180° on a plan. Molar mass of CO2 is 44.01 g/mol .Oxygen has six valence electrons and each hydrogen has one valence electron, producing the Lewis electron structure. Figure 10.2.2 10.2. 2: (CC BY-NC-SA; anonymous) 3. With two bonding pairs and two lone pairs, the structure is designated as AX 2 E 2 with a total of four electron pairs. In this video we look at the electron geometry for CO2 (Carbon Dioxide). Because the Carbon dioxide molecule has two electron domains (two oxygen atoms and n.
The rest 28 electrons are non-bonding electrons. Carbon completes its octet by forming bonds with four chlorine atoms. The hybridization of CCl4 is sp3 and has a tetrahedral shape. The bond angle is 109.8 degrees between the lone pairs of electrons and it is nonpolar. Carbon Tetrachloride was first synthesized as a by-product in the . The geometry of BCl3 BCl 3 is also given in Figure 7.2: it is trigonal planar, with all four atoms lying in the same plane, and all Cl−B−Cl Cl − B − Cl bond angles equal to 120o 120 o. The three Cl Cl atoms form an equilateral triangle. The Boron atom has only three pairs of valence shell electrons in BCl3 BCl 3.

A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of CO2 including a description of the CO2 bond angles.We can see that there are only two atoms attached to the .
A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of CO2 including a description of the CO2 bond angles.We can see that there are only two atoms attached to the .co2 electron pair geometry and molecular geometry A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of CO2 including a description of the CO2 bond angles.We can see that there are only two atoms attached to the . The Lewis structure of H 2 O indicates that there are four regions of high electron density around the oxygen atom: two lone pairs and two chemical bonds: Figure 7.6.9 7.6. 9. Thus, the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular structure is bent with an angle slightly less than 109.5°.
The CO2 molecular geometry and bond angles notes conclude that the CO2 or carbon dioxide contains a total of 16 valence electrons which show on the outer shell of atoms, ie, four atoms of the carbon as well as 12 of two atoms of oxygen. With this, we can effortlessly draw the diagram of the Lewis dot of CO2 by adjusting two double bonds amid . SO2 Molecular Geometry and Shape. To determine the molecular geometry of Sulfur Dioxide, we must observe its Lewis structure. There are two Oxygen atoms bonded to the central Sulfur .2. The carbon atom forms two double bonds. Each double bond is a group, so there are two electron groups around the central atom. Like BeH 2, the arrangement that minimizes repulsions places the groups 180° apart. 3. Once again, both groups around the central atom are bonding pairs (BP), so CO 2 is designated as AX 2.
Predicting Electron-pair Geometry and Molecular Structure: CO 2 and BCl 3 Predict the electron-pair geometry and molecular structure for each of the following: (a) carbon dioxide, CO 2, a molecule produced by the combustion of fossil fuels (b) boron trichloride, BCl 3, an important industrial chemical. Solution (a) We write the Lewis structure . Carbonate ion (CO32-) Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry or shape, electron geometry, bond angle, formal charge, hybridization. CO 32- is the chemical formula for carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion composed of 1 carbon and 3 oxygen atoms. It is present in a carbonate salt i.e., a salt of carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ).The Electron Pair Geometry of a molecule is determined by the total number of electron pairs around a central atom. Electron pairs are the bonded electrons, lone pairs and single unpaired electrons. . Electron pairs are arranged at a 180° angle in a linear molecule. Example: Carbon dioxide. Total number of electron pairs = ½ X [(number of .D With two nuclei around the central atom and one lone pair of electrons, the molecular geometry of SnCl 2 is bent, . The carbon in the –N=C=O fragment is doubly bonded to both nitrogen and oxygen, which in the VSEPR model gives carbon a total of two electron pairs. The N=C=O angle should therefore be 180°, or linear. The three fragments . Together, the four sp 3 hybrid orbitals produce an approximately tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs, which agrees with the molecular geometry predicted by the VSEPR model. A The CHCl 3 molecule has four valence electrons around the central atom. In the VSEPR model, the carbon atom has four electron pairs, and the .Since water has two lone pairs it's molecular shape is bent. According to the VSEPR theory, the electrons want to minimize repulsion, so as a result, the lone pairs are adjacent from each other. CO 2: Carbon dioxide has two electron groups and no lone pairs. Carbon dioxide is therefore linear in electron-group geometry and in molecular .
Etihad Airways (EY) seat map listing. Etihad Airways was founded in July 2003 and started operations in November 2003. The airline is the second-largest national airline in the United Arab Emirates. It is headquartered in Khalifa City, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Abu Dhabi International Airport is Etihad Airways' main hub.
co2 electron pair geometry and molecular geometry|CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar